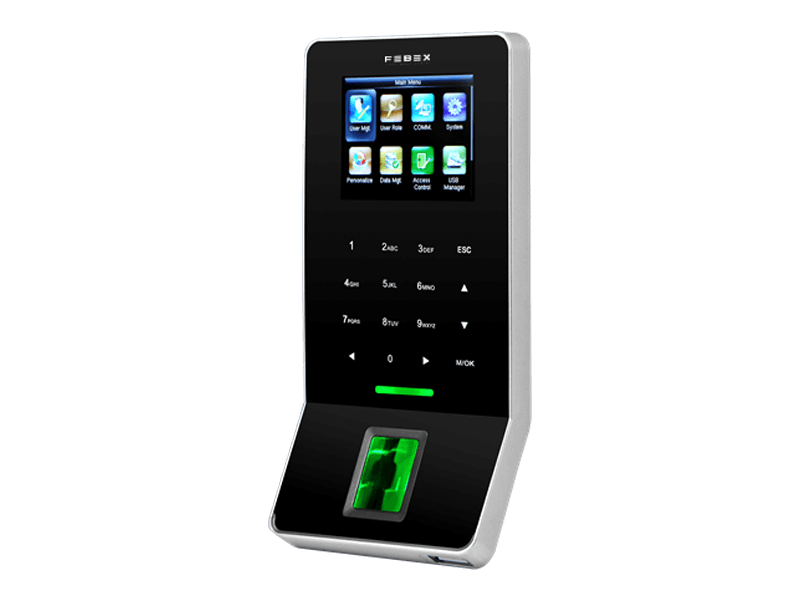
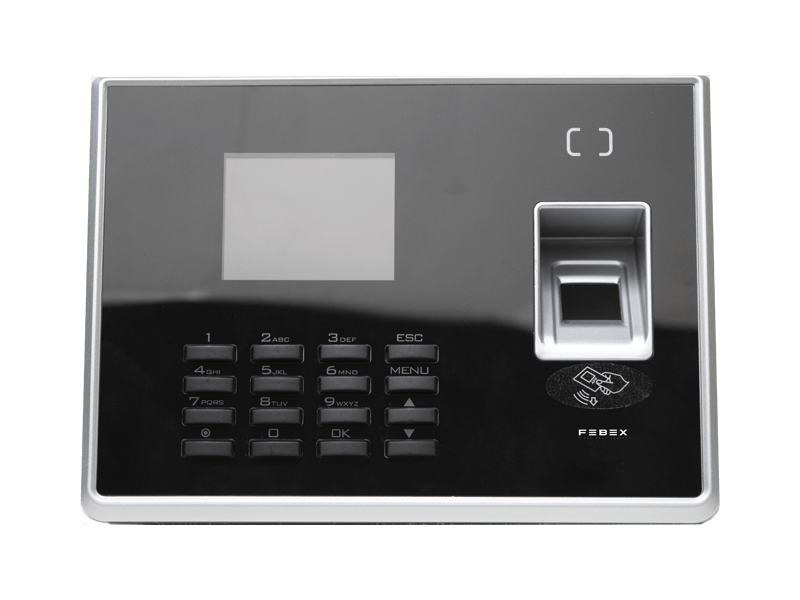
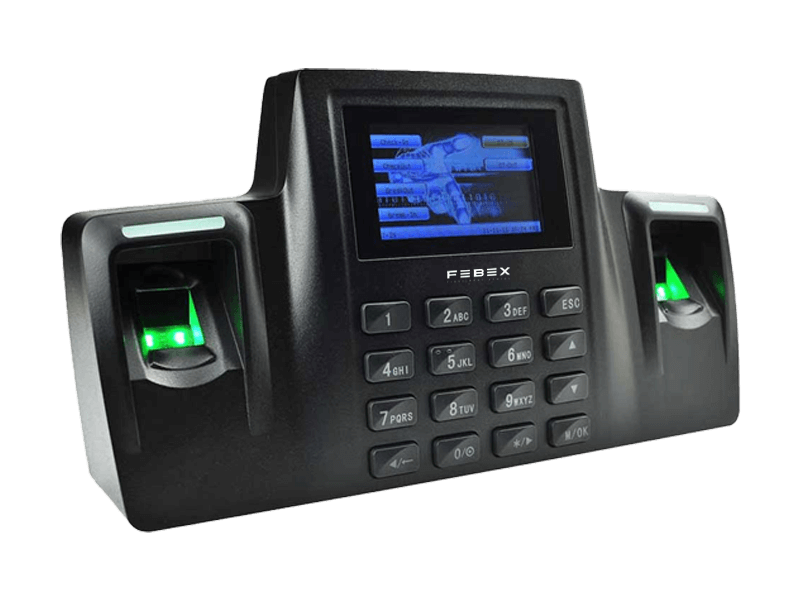
Febex The Evolution of Security: Fingerprint Access Control Systems
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of security technology, fingerprint access control systems have emerged as a cutting-edge and highly effective means of safeguarding physical spaces and digital information. This article explores the principles behind fingerprint-based access control, its advantages, potential challenges, and the role it plays in shaping the future of security systems.
The Basics of Fingerprint Access Control:
Fingerprint access control systems leverage the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual’s fingertips for identification and authentication. Each person’s fingerprint is distinct, making it an ideal biometric identifier. When integrated into access control systems, fingerprints serve as an impenetrable key, granting or denying access based on pre-authorized fingerprints stored in a secure database.
Advantages of Fingerprint Access Control:
- Unparalleled Security: Fingerprint patterns are incredibly unique, making the chances of unauthorized access extremely low. Unlike traditional access methods such as keycards or passwords, fingerprints are not easily replicable or shareable.
- Convenience and Speed: Fingerprint access is quick and convenient. Authorized individuals can gain entry with a simple touch, eliminating the need for physical keys or memorized codes. This efficiency is particularly valuable in high-traffic areas.
- Reduced Risk of Unauthorized Access: Fingerprint access control eliminates the risk of unauthorized access due to lost or stolen keycards, forgotten passwords, or shared access credentials. The system ensures that only individuals with pre-authorized fingerprints can enter secure areas.
- Audit Trail and Accountability: Fingerprint access control systems often include features such as audit trails, logging every entry and exit. This not only enhances security but also provides a valuable tool for tracking movement and maintaining accountability.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and storing biometric data, including fingerprints, raises privacy concerns. Implementers of fingerprint access control systems must prioritize robust security measures to protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Cost of Implementation: While the long-term benefits are substantial, the initial cost of implementing fingerprint access control systems can be higher than traditional methods. However, advancements in technology are gradually reducing these costs.
- Environmental Factors: External factors, such as dirt, moisture, or extreme temperatures, can affect the accuracy of fingerprint scanners. Implementers must choose devices that are resilient to environmental challenges.
Future Trends and Innovations:
- Integration with Other Technologies: Fingerprint access control is increasingly being integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), to create smarter and more adaptive security systems.
- Mobile Access Control: Mobile devices equipped with fingerprint sensors are becoming common tools for access control. This trend allows for greater flexibility and remote management of access permissions.
- Continuous Authentication: Advancements in biometric technology are leading to the development of continuous authentication systems, where a person’s identity is verified continuously rather than just during the initial access attempt.
Conclusion:
Fingerprint access control systems represent a significant leap forward in the realm of security technology. Their combination of unmatched security, convenience, and accountability positions them as a key player in shaping the future of access control. As these systems continue to evolve, addressing privacy concerns and staying abreast of technological innovations will be essential to maximizing their potential in securing physical and digital spaces.